The Role Of Economy In Shaping Our Modern World
Economy plays a crucial role in determining the well-being of societies around the globe. It influences everything from job opportunities to the standard of living, impacting individuals' daily lives in profound ways. Understanding the economy is not just for economists; it's essential for everyone who wants to make informed decisions about their financial future.
In today's interconnected world, the economy has become a complex system that affects every aspect of life. From the food we eat to the technology we use, the economy shapes how goods and services are produced, distributed, and consumed. This intricate network of transactions and relationships forms the backbone of modern society.
As we delve deeper into the workings of the global economy, it becomes increasingly clear how interconnected economies are across nations. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the economy, breaking down complex concepts into digestible information that anyone can grasp. Whether you're a student, professional, or simply curious about the world of economics, this guide is for you.
Table of Contents
- What is Economy?
- Types of Economies
- Economic Indicators
- Impact of Globalization on Economy
- Role of Government in Economy
- Economic Theories and Their Relevance
- Sustainability and Economy
- Future Trends in Economy
- Challenges Facing the Economy
- Conclusion
What is Economy?
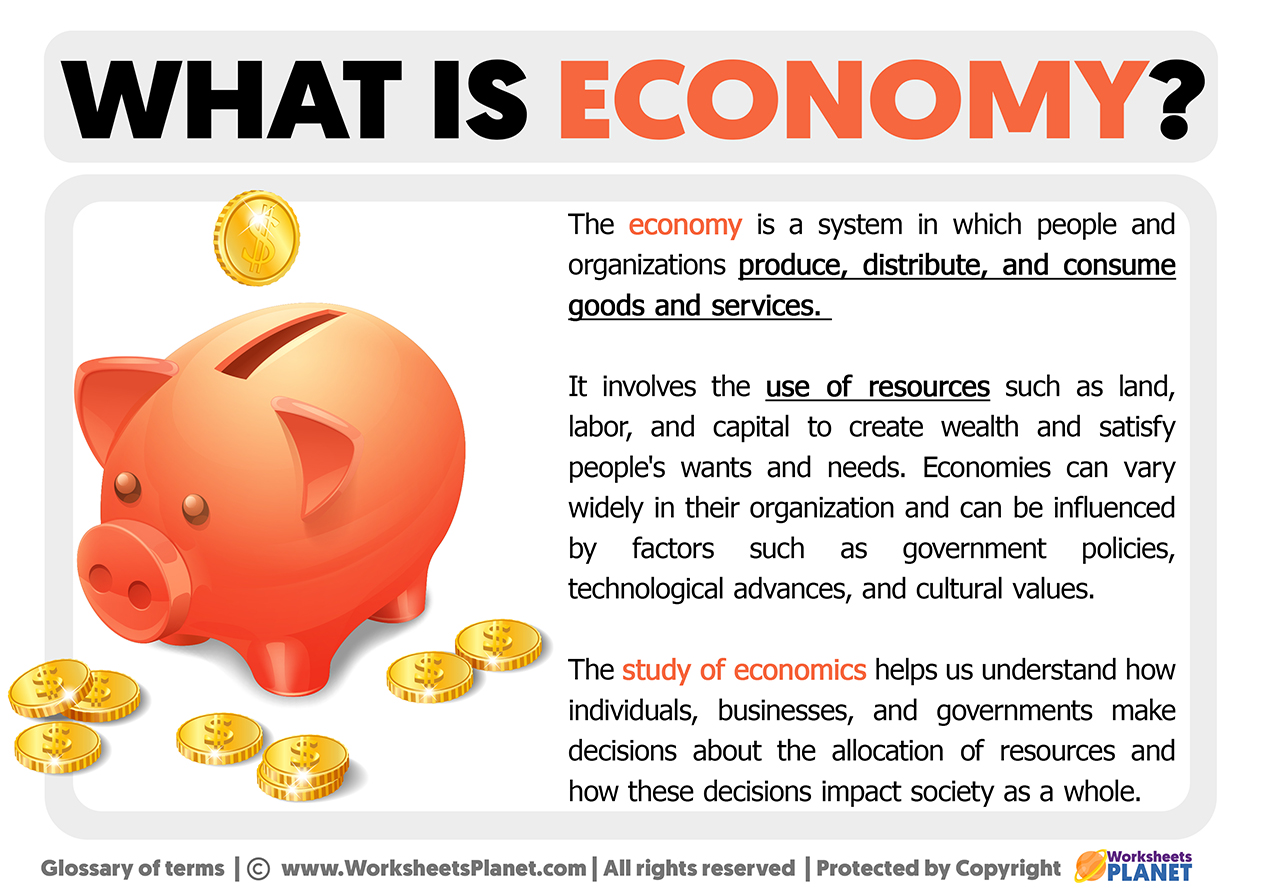
An economy refers to the system by which goods and services are produced, distributed, and consumed within a particular region or country. It encompasses all activities related to the production and consumption of goods and services, including trade, finance, and labor markets. The economy operates on principles of supply and demand, where producers aim to meet consumer needs while maximizing profits.
Economies can vary significantly depending on cultural, political, and geographical factors. For instance, some countries rely heavily on agriculture, while others focus on manufacturing or service industries. Understanding the structure and dynamics of an economy is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike.
Key Components of an Economy
Several key components form the foundation of any economy:
- Kyle Richards Leaving Rhobh
- Alachua County Early Voting
- Michael Peterson Books
- Fiaschetteria West Village
- Rob Moore Executive
- Resources: Natural, human, and capital resources are essential for producing goods and services.
- Production: The process of creating goods and services using available resources.
- Consumption: The use of goods and services by individuals and businesses.
- Exchange: The buying and selling of goods and services in markets.
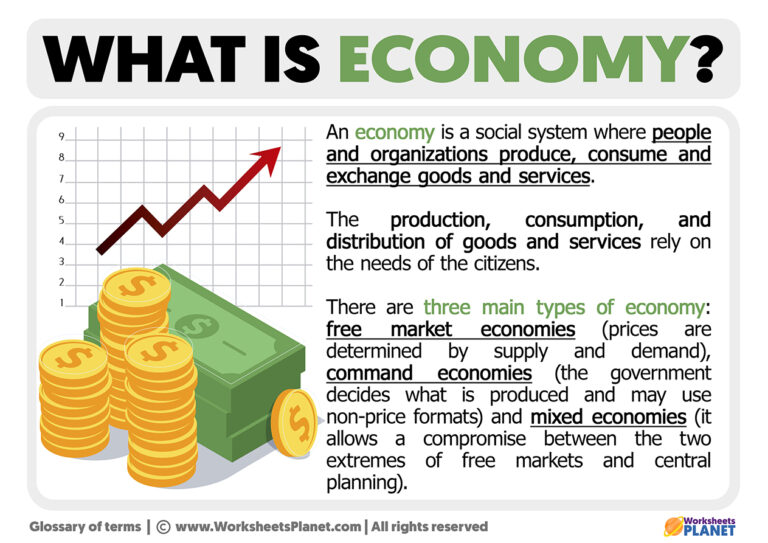
Types of Economies
Economies can be classified into different types based on how resources are allocated and decisions are made. The three main types of economies are market economies, command economies, and traditional economies.
Market Economies
In a market economy, decisions about investment, production, and distribution are driven by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand. Businesses operate independently, and competition plays a key role in determining prices and quality.
Command Economies
A command economy is one in which the government makes all decisions about the production and distribution of goods and services. This type of economy is often associated with socialist or communist countries, where the state controls major industries and resources.
Traditional Economies
Traditional economies rely on customs, history, and time-honored beliefs to decide what to produce, how to produce it, and to whom to distribute it. This type of economy is common in rural or tribal communities where traditions and cultural practices play a significant role.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators are statistics that help us understand the current state of the economy. These indicators provide valuable insights into economic performance and can help predict future trends. Some of the most commonly used economic indicators include:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): The total value of all goods and services produced within a country over a specific period.
- Inflation Rate: The rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, and subsequently, purchasing power is falling.
- Unemployment Rate: The percentage of the labor force that is unemployed but actively seeking employment.
Impact of Globalization on Economy
Globalization has significantly transformed the global economy by increasing interconnectedness between countries. It has facilitated the movement of goods, services, capital, and technology across borders, leading to increased trade and investment opportunities. However, globalization also poses challenges, such as job displacement and income inequality.
Benefits of Globalization
Globalization has brought numerous benefits to the global economy, including:
- Access to a wider range of goods and services.
- Increased competition, leading to better quality and lower prices.
- Creation of new markets and opportunities for businesses.
Challenges of Globalization
Despite its advantages, globalization also presents challenges, such as:
- Job displacement due to outsourcing.
- Environmental degradation caused by increased industrial activity.
- Cultural homogenization and loss of local traditions.
Role of Government in Economy
Governments play a crucial role in managing and regulating the economy. They create policies and regulations to ensure stability, promote growth, and protect consumers and workers. Fiscal and monetary policies are two primary tools used by governments to influence economic activity.
Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy involves government spending and taxation. By adjusting these variables, governments can influence economic activity and achieve desired outcomes, such as reducing unemployment or controlling inflation.
Monetary Policy
Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by central banks to control the money supply and interest rates. These actions can stimulate or slow down economic growth, depending on the current economic conditions.
Economic Theories and Their Relevance
Economic theories provide frameworks for understanding how economies function and predicting future trends. Some of the most influential economic theories include:
- Classical Economics: Emphasizes the importance of free markets and minimal government intervention.
- Keynesian Economics: Focuses on the role of government in managing economic activity, particularly during times of recession or depression.
- Supply-Side Economics: Advocates for reducing taxes and regulations to stimulate economic growth.
Sustainability and Economy
Sustainability has become a critical concern for economies around the world. As environmental issues like climate change and resource depletion become more pressing, there is a growing need for sustainable economic practices. Green economics and circular economies are two approaches that aim to balance economic growth with environmental protection.
Green Economics
Green economics focuses on integrating environmental considerations into economic decision-making. It emphasizes the importance of reducing pollution, conserving natural resources, and promoting renewable energy sources.
Circular Economy
A circular economy is an economic system aimed at eliminating waste and the continual use of resources. It promotes recycling, reusing, and reducing waste to create a more sustainable economic model.
Future Trends in Economy
The global economy is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, demographic shifts, and changing consumer preferences. Some of the key trends shaping the future of the economy include:
- Digitization: The increasing use of digital technologies in business operations and transactions.
- Artificial Intelligence: The integration of AI in various industries, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Sustainability: Growing emphasis on environmentally friendly practices and renewable energy sources.
Challenges Facing the Economy
Despite its progress, the global economy faces several challenges that could hinder future growth and development. These challenges include:
- Income Inequality: The growing gap between the rich and the poor, which can lead to social unrest and political instability.
- Climate Change: The adverse effects of global warming on economic activities and natural resources.
- Technological Disruption: The impact of automation and AI on jobs and industries.
Conclusion
The economy is a complex and dynamic system that affects every aspect of our lives. Understanding its principles and dynamics is essential for making informed decisions about our financial future. From the different types of economies to the challenges facing the global economy, this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the key aspects of the economy.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and insights in the comments section below. Your feedback helps us improve and create content that better serves your needs. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site to deepen your knowledge of various economic topics.
Together, let's continue to learn and grow in our understanding of the economy and its impact on our world.
- Are The 3 Stooges Still Alive
- Georgetown Texas 3d Printed Homes
- East Coast Thrift Spencer Ma Opening Hours
- Mary J Blige Logo
- Omar Gooding Brother
What Is Economy
What is Economy Definition & Meaning of Economy