Measles Outbreaks In The United States: Understanding The Epidemic
Measles outbreaks in the United States have become a growing concern over the past few decades. Despite the widespread availability of vaccines, the resurgence of measles has highlighted gaps in public health awareness and vaccine coverage. This infectious disease, once thought to be eradicated, is now making headlines due to its alarming comeback. Understanding the factors contributing to this phenomenon is crucial for safeguarding public health.
Measles, a highly contagious viral illness, has been one of the leading causes of preventable deaths worldwide. While global efforts to vaccinate children have significantly reduced the incidence of measles, the United States has not been immune to its resurgence. This article aims to explore the reasons behind the outbreaks, their implications, and potential solutions to combat this growing health crisis.
By examining the history of measles, vaccine hesitancy, and current public health strategies, we can better understand the challenges faced by healthcare systems. Furthermore, we will delve into the importance of community immunity and the role of education in preventing future outbreaks. Stay informed, as your knowledge can make a difference in protecting yourself and those around you.
- Jarred Harper Movies And Tv Shows
- Rucci Rims Price
- Brown Line Stations
- Best Restaurants Near Nederlander Theater Nyc
- Chief Keef Autistic
Table of Contents
- History of Measles in the United States
- Causes of Measles Outbreaks
- Symptoms of Measles
- Vaccination Against Measles
- Understanding Vaccine Hesitancy
- The Role of Community Immunity
- Public Health Strategies to Combat Measles
- Measles Statistics in the United States
- A Global Perspective on Measles
- Prevention and Future Outlook
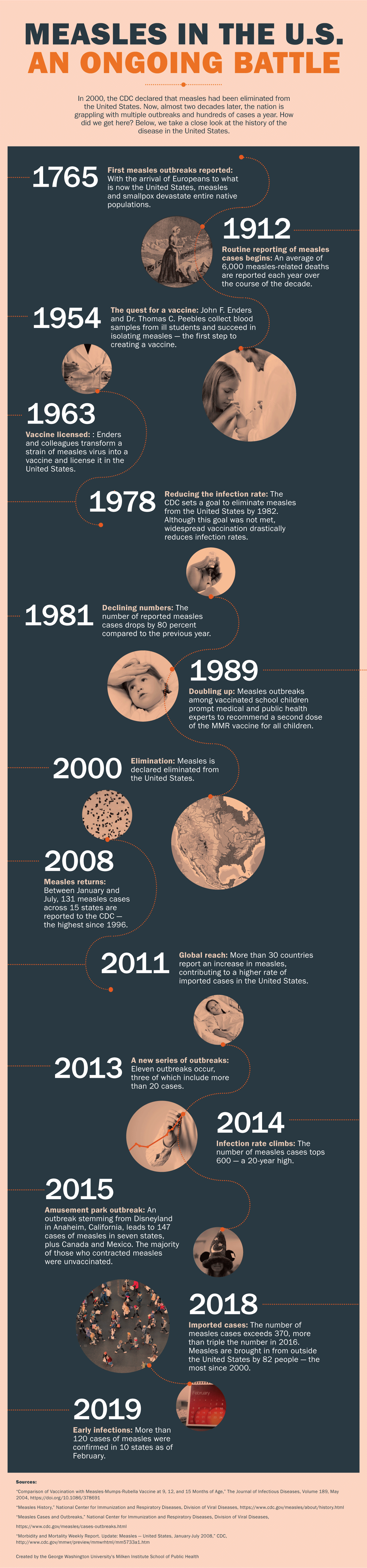
History of Measles in the United States
Measles has a long and complex history in the United States. Before the introduction of the measles vaccine in 1963, the disease was widespread, causing millions of cases and thousands of deaths annually. The vaccine marked a turning point, leading to a significant decline in cases. By 2000, measles was declared eliminated in the U.S., thanks to sustained vaccination efforts.
However, the declaration of elimination did not mean the end of measles. International travel and vaccine hesitancy have contributed to the re-emergence of outbreaks. In recent years, clusters of measles cases have been reported in various states, raising concerns about the nation's public health infrastructure.
Key Milestones in Measles Eradication
- 1963: Introduction of the measles vaccine.
- 1989: Implementation of the two-dose vaccination schedule.
- 2000: Measles declared eliminated in the U.S.
- 2019: Largest measles outbreak in nearly three decades.
Causes of Measles Outbreaks
Several factors contribute to the resurgence of measles outbreaks in the United States. One of the primary causes is vaccine hesitancy, where individuals or communities refuse or delay vaccination due to misinformation or personal beliefs. Additionally, international travel facilitates the importation of measles cases from countries where the disease is still endemic.
Factors Contributing to Outbreaks
- Vaccine hesitancy and misinformation.
- Importation of cases from international travelers.
- Low vaccination coverage in certain communities.
- Weak public health infrastructure in some regions.
Symptoms of Measles
Measles is characterized by a range of symptoms that typically appear 10-14 days after exposure. Early symptoms include high fever, cough, runny nose, and red, watery eyes. A few days later, a red rash develops, starting from the face and spreading to the rest of the body. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Common Symptoms of Measles
- High fever.
- Cough.
- Runny nose.
- Red, watery eyes.
- Red rash.
Vaccination Against Measles
Vaccination remains the most effective way to prevent measles. The measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine is administered in two doses, with the first dose given at 12-15 months of age and the second dose at 4-6 years. The vaccine is safe and highly effective, providing lifelong immunity against the disease.
Despite its proven efficacy, vaccine hesitancy has led to declining vaccination rates in some areas. Addressing misinformation and promoting vaccine education are essential steps in increasing vaccination coverage.
Effectiveness of the MMR Vaccine
- 93% effective after one dose.
- 97% effective after two doses.
Understanding Vaccine Hesitancy
Vaccine hesitancy refers to the reluctance or refusal to vaccinate despite the availability of vaccines. This phenomenon is influenced by a variety of factors, including misinformation, mistrust in healthcare systems, and personal beliefs. Social media platforms have played a significant role in spreading false information about vaccines, further complicating efforts to increase vaccination rates.
Educational campaigns and community engagement are critical in addressing vaccine hesitancy. By providing accurate information and building trust, public health officials can encourage more individuals to vaccinate themselves and their families.
Causes of Vaccine Hesitancy
- Misinformation and myths about vaccines.
- Mistrust in healthcare systems.
- Religious or philosophical objections.
- Lack of access to healthcare services.
The Role of Community Immunity
Community immunity, also known as herd immunity, plays a vital role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases like measles. When a significant portion of the population is vaccinated, it creates a protective barrier that reduces the likelihood of outbreaks. This is especially important for protecting vulnerable individuals who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants and those with compromised immune systems.
However, when vaccination rates decline, community immunity is weakened, increasing the risk of outbreaks. Public health campaigns must emphasize the importance of vaccination not only for individual protection but also for the broader community.
Benefits of Community Immunity
- Reduces the spread of infectious diseases.
- Protects vulnerable populations.
- Strengthens public health infrastructure.
Public Health Strategies to Combat Measles
Public health officials employ various strategies to combat measles outbreaks. These include monitoring vaccination coverage, implementing vaccination mandates, and conducting outreach programs in underserved communities. Collaboration between federal, state, and local health departments is essential for a coordinated response to outbreaks.
Additionally, public health campaigns aim to educate the public about the importance of vaccination and dispel myths surrounding vaccines. By fostering trust and promoting accurate information, these campaigns can significantly reduce the incidence of measles.
Strategies for Measles Prevention
- Monitoring vaccination coverage.
- Implementing vaccination mandates.
- Conducting outreach programs.
- Disseminating accurate information.
Measles Statistics in the United States
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reveal concerning trends in measles outbreaks. In 2019, the United States experienced the largest number of measles cases in nearly three decades, with over 1,200 cases reported. This surge was primarily attributed to outbreaks in under-vaccinated communities.
While vaccination rates remain high overall, pockets of low coverage have emerged, creating vulnerabilities in the public health system. Continued monitoring and intervention are necessary to prevent further outbreaks.
Key Statistics
- 2019: 1,282 cases reported.
- 2020: 13 cases reported.
- 2021: 49 cases reported.
A Global Perspective on Measles
Measles is not only a concern in the United States but also a global health issue. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), measles remains one of the leading causes of vaccine-preventable deaths worldwide. In 2020, an estimated 9 million cases and 142,000 deaths were reported globally.
International efforts to combat measles include the Global Vaccine Action Plan, which aims to eliminate the disease in five WHO regions by 2020. While progress has been made, challenges such as vaccine inequity and political instability hinder efforts in some countries.
Global Measles Statistics
- 2020: 9 million cases reported.
- 2020: 142,000 deaths reported.
- 2021: Continued efforts to increase vaccination coverage.
Prevention and Future Outlook
Preventing measles outbreaks requires a multifaceted approach that includes increasing vaccination coverage, addressing vaccine hesitancy, and strengthening public health infrastructure. Continued research and development of vaccines are also essential for staying ahead of emerging threats.
The future outlook for measles prevention depends on global cooperation and commitment to eradicating the disease. By working together, nations can achieve a world free from measles, protecting future generations from its devastating effects.
Steps for Prevention
- Increase vaccination coverage.
- Address vaccine hesitancy.
- Strengthen public health infrastructure.
- Support global vaccination efforts.
Kesimpulan
Measles outbreaks in the United States highlight the ongoing challenges faced by public health systems. While significant progress has been made in reducing the incidence of measles, vaccine hesitancy and international travel continue to pose risks. By understanding the causes of outbreaks and implementing effective prevention strategies, we can work towards a future free from measles.
We encourage readers to take action by ensuring they and their loved ones are up-to-date with vaccinations. Share this article with others to promote awareness and join the global effort to eradicate measles. Together, we can protect our communities and safeguard public health for generations to come.
- Casting Director Allison Jones
- Neil Ellice Height
- Vikings Kicker 2023
- Elise Marie Smith
- Why Did Duck Dynasty Get Canceled
A History of Measles in the United States Online Public Health
What you need to know about measles

A History of Measles Outbreaks in United States VAXOPEDIA