Understanding Antidepressants: A Comprehensive Guide To Treatment, Types, And Effects
Antidepressants are medications designed to treat depression and other mood disorders, offering hope to millions of people worldwide. Depression is a serious mental health condition that affects millions of people globally, and antidepressants play a crucial role in managing its symptoms. These medications work by altering the balance of chemicals in the brain, helping to improve mood, sleep, appetite, and concentration. Understanding how antidepressants work, their types, and potential side effects is essential for anyone considering this treatment option.
Depression is more than just feeling sad or experiencing temporary emotional distress. It is a complex condition that can interfere with daily life, relationships, and overall well-being. Antidepressants are one of the most effective treatments available, but they are often misunderstood or misrepresented. In this article, we aim to provide a clear, evidence-based overview of antidepressants, their benefits, and potential drawbacks.
Whether you are someone who is considering antidepressants for yourself or a loved one, understanding the science behind these medications is crucial. This article will explore the different types of antidepressants, how they work, potential side effects, and important considerations for safe and effective use. Let’s dive in to learn more about this essential treatment option.
- Duck Dynasty Cancelled
- Jarred Harper Movies And Tv Shows
- Shonda Rhimes Spouse
- Muscle Man Voiced By
- Why Is Needlepoint So Expensive
Table of Contents
- What Are Antidepressants?
- How Do Antidepressants Work?
- Types of Antidepressants
- Benefits of Antidepressants
- Side Effects and Risks
- Common Misconceptions About Antidepressants
- Choosing the Right Antidepressant
- Long-Term Use of Antidepressants
- Alternatives to Antidepressants
- Tips for Safe Use
What Are Antidepressants?
Antidepressants are prescription medications primarily used to treat depression, but they are also effective for other mental health conditions such as anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These medications work by influencing neurotransmitters in the brain, specifically serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, which are chemicals responsible for regulating mood, emotions, and behavior.
There are several classes of antidepressants, each with its own mechanism of action and potential benefits. While they are not a cure for depression, antidepressants can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life when used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes therapy and lifestyle changes.
Key Facts About Antidepressants
- Antidepressants are prescribed by healthcare professionals, including psychiatrists and primary care physicians.
- They are not addictive in the traditional sense, but sudden discontinuation can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms.
- Antidepressants may take several weeks to show full effects, so patience and consistency are key.
How Do Antidepressants Work?
Antidepressants work by altering the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals between nerve cells. Imbalances in these chemicals, particularly serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, are thought to contribute to depression and other mood disorders.
- Pel%C3%ADculas Y Programas De Tv De Ethan Slater
- Doug Arby S
- Are The 3 Stooges Still Alive
- Babi Xavier
- Moriah Elizabeth Yearbook
By increasing the availability of these neurotransmitters in the brain, antidepressants help improve mood, reduce anxiety, and enhance overall emotional well-being. The exact mechanisms of action vary depending on the type of antidepressant, but the goal is always to restore balance to the brain’s chemistry.
Neurotransmitter Focus
- Serotonin: Often referred to as the "feel-good" chemical, serotonin regulates mood, sleep, and appetite.
- Norepinephrine: Plays a role in alertness, energy, and motivation.
- Dopamine: Associated with pleasure, reward, and motivation.
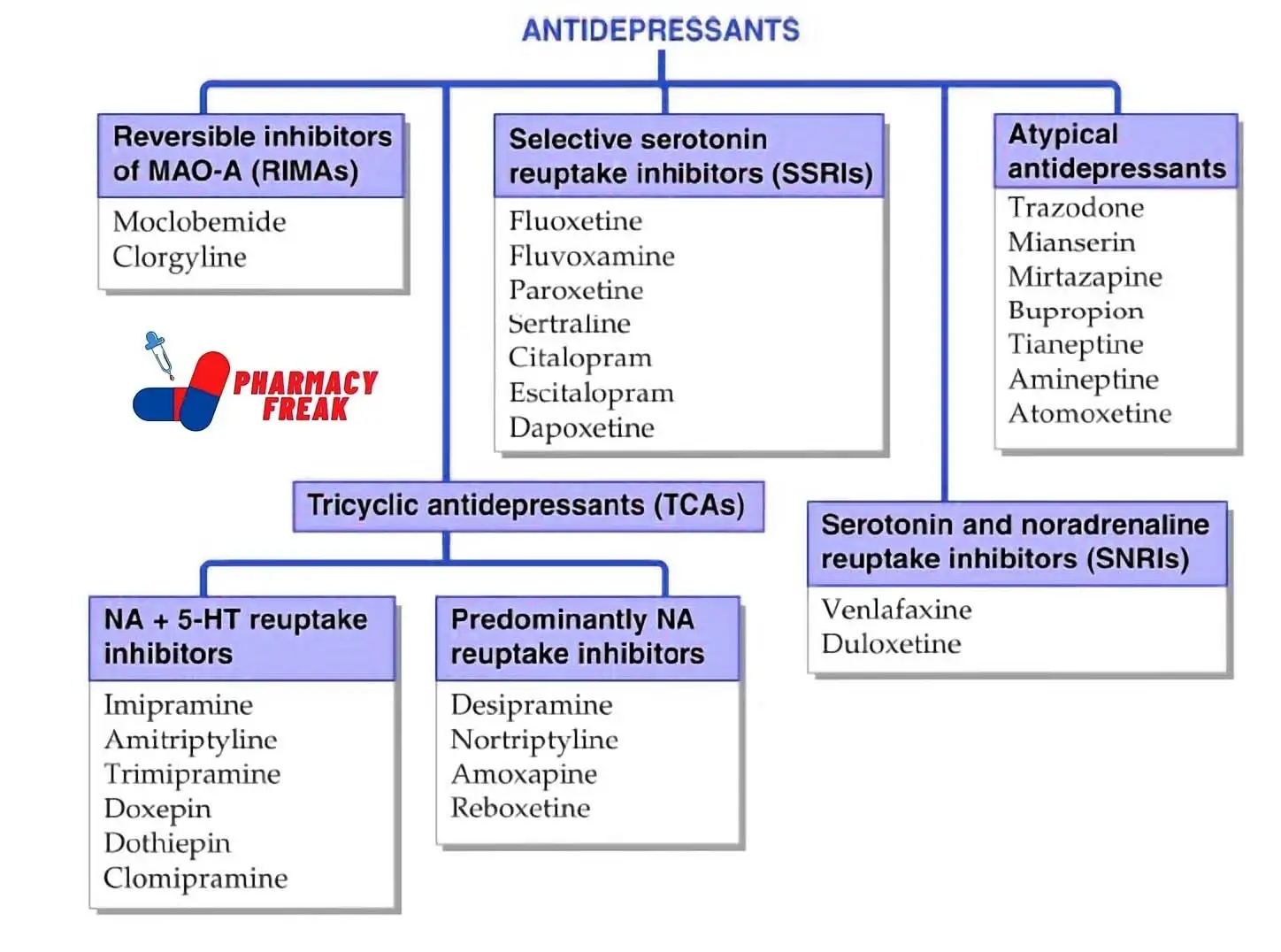
Types of Antidepressants
There are several classes of antidepressants, each with its own unique mechanism of action. Understanding the differences between these types can help patients and healthcare providers choose the most appropriate treatment option.
1. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
SSRIs are the most commonly prescribed antidepressants. They work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain. Examples include fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft), and escitalopram (Lexapro).
2. Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
SNRIs increase the levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine. Common examples include venlafaxine (Effexor) and duloxetine (Cymbalta).
3. Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
TCAs are older antidepressants that affect serotonin and norepinephrine. While effective, they often come with more side effects compared to newer medications. Examples include amitriptyline and imipramine.
4. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
MAOIs are another older class of antidepressants that work by inhibiting the enzyme monoamine oxidase. They require dietary restrictions and are typically reserved for cases where other treatments have failed.
Benefits of Antidepressants
Antidepressants offer numerous benefits for individuals struggling with depression and related conditions. They can help alleviate symptoms such as sadness, hopelessness, fatigue, and lack of interest in activities. Additionally, antidepressants can improve sleep, appetite, and concentration, allowing individuals to regain control over their lives.
When combined with therapy and lifestyle changes, antidepressants can be highly effective in managing depression and preventing relapse. They are also used to treat anxiety disorders, OCD, PTSD, and chronic pain, making them versatile treatment options for a range of mental health conditions.
Key Benefits
- Improved mood and emotional well-being
- Enhanced sleep and appetite
- Increased energy and motivation
- Reduced anxiety and stress
Side Effects and Risks
While antidepressants are generally safe and effective, they can cause side effects, especially during the initial stages of treatment. Common side effects include nausea, dizziness, weight gain, sexual dysfunction, and insomnia. Most side effects are mild and temporary, improving as the body adjusts to the medication.
In rare cases, antidepressants may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts, particularly in young adults and teenagers. It is essential to monitor these symptoms closely and report any concerns to a healthcare provider immediately.
Managing Side Effects
- Start with a low dose and gradually increase as tolerated.
- Take medications with food to reduce nausea.
- Stay hydrated and maintain a healthy diet.
- Communicate openly with your healthcare provider about any side effects.
Common Misconceptions About Antidepressants
Despite their widespread use, antidepressants are often surrounded by myths and misconceptions. Some people believe they are addictive, while others think they will change their personality. In reality, antidepressants are not habit-forming and do not alter one’s core identity. Instead, they help balance brain chemistry, allowing individuals to function more effectively.
Another common misconception is that antidepressants are a quick fix or a substitute for therapy. While they can provide relief from symptoms, they work best when combined with other treatment approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or interpersonal therapy (IPT).
Debunking Myths
- Antidepressants are not addictive.
- They do not change your personality.
- They are most effective when used alongside therapy.
Choosing the Right Antidepressant
Selecting the right antidepressant involves considering several factors, including the severity of symptoms, medical history, and individual preferences. Healthcare providers often start with SSRIs due to their favorable side effect profile and efficacy. However, if one medication does not work or causes intolerable side effects, switching to another class of antidepressants may be necessary.
Genetic testing is also becoming a valuable tool in personalized medicine, helping to identify which medications are most likely to be effective based on an individual’s genetic makeup. This approach can save time and reduce trial-and-error when choosing an antidepressant.
Factors to Consider
- Symptom severity and type
- Patient’s medical history
- Potential side effects
- Genetic testing results
Long-Term Use of Antidepressants
For some individuals, long-term use of antidepressants may be necessary to maintain mental health stability. However, extended use requires careful monitoring to ensure the medication remains effective and safe. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify any emerging side effects or changes in symptoms.
It is important to note that antidepressants are not meant to be taken indefinitely without reassessment. Periodic evaluations can determine whether a lower dose or alternative treatment is appropriate. Gradual tapering off the medication, rather than abrupt discontinuation, is recommended to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
Monitoring Long-Term Use
- Schedule regular check-ins with your healthcare provider.
- Be mindful of any changes in mood or side effects.
- Discuss tapering plans if discontinuation is desired.
Alternatives to Antidepressants
While antidepressants are effective for many people, they are not the only treatment option available. Alternative approaches such as therapy, lifestyle changes, and complementary therapies can also play a significant role in managing depression.
Therapeutic interventions like CBT, IPT, and mindfulness-based therapy can help individuals develop coping strategies and improve emotional resilience. Lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep, can also support mental health. In some cases, herbal supplements like St. John’s Wort or omega-3 fatty acids may be considered, though they should be used under medical supervision.
Complementary Therapies
- Mindfulness meditation
- Yoga and tai chi
- Art or music therapy
Tips for Safe Use
Using antidepressants safely involves following a few key guidelines. Always take medications as prescribed, avoid skipping doses, and never stop taking them abruptly without consulting a healthcare provider. Keep track of any side effects or changes in symptoms and report them promptly.
Store medications securely, out of reach of children and pets. If you are taking other medications or supplements, inform your healthcare provider to avoid potential interactions. Lastly, maintain open communication with your treatment team to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Safe Usage Guidelines
- Follow prescribed dosing instructions.
- Avoid abrupt discontinuation.
- Report any side effects immediately.
Conclusion
Antidepressants are a vital tool in the treatment of depression and related mental health conditions. By understanding how they work, their benefits, and potential risks, individuals can make informed decisions about their care. While antidepressants are not a one-size-fits-all solution, they offer hope and relief to millions of people worldwide.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from learning about antidepressants. If you have any questions or insights, feel free to leave a comment below. Remember, seeking professional help is the first step toward recovery, and there is no shame in reaching out for support.
References:
- Mayo Clinic. (2022). Antidepressants: Selecting one that's right for you.
- National Institute of Mental Health. (2021). Depression.
- World Health Organization. (2023). Mental health.
- Vezenkov Buyout
- Sharesight Portfolio Tracker
- Elvin On Cosby Show
- Secretive Stash Sea Of Thieves
- Turks And Timbers
Classification of Antidepressants Pharmacy Freak

Antidepressants an update Zen Garage

Antidepressants Ineffectiveness and Risks Faith Seeking Understanding